2D image rotation performance#
This example demonstrates how to create a basic rotation using the TensorSpline API and comparing against Scipy’s.
Imports#
Import necessary libraries.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
from scipy import ndimage, datasets
from splineops.interpolate.tensorspline import TensorSpline
Calculate inscribed rectangle bounds from image#
Calculate the bounds for the largest rectangle that can be inscribed within a circle, which itself is inscribed within the original image, based on the image array directly.
def calculate_inscribed_rectangle_bounds_from_image(image):
"""
Calculate the bounds for the largest rectangle that can be inscribed
within a circle, which itself is inscribed within the original image,
based on the image array directly.
The rectangle and the circle are centered within the original image.
Parameters:
- image: The input image as a 2D or 3D numpy array.
Returns:
- A tuple (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) representing the bounds for cropping.
"""
# Extract image dimensions
height, width = image.shape[:2]
# Calculate the radius of the inscribed circle
radius = min(width, height) / 2
# The side length of the square (largest inscribed rectangle in a circle)
side_length = radius * np.sqrt(2)
# Calculate the center of the image
cx, cy = width / 2, height / 2
# Calculate the bounds of the largest inscribed rectangle
x_min = int(cx - side_length / 2)
y_min = int(cy - side_length / 2)
x_max = int(cx + side_length / 2)
y_max = int(cy + side_length / 2)
return np.array([x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max])
Crop image to bounds#
Crop an image to the specified bounds.
def crop_image_to_bounds(image, bounds):
"""
Crop an image to the specified bounds.
Parameters:
- image: The input image as a 2D numpy array.
- bounds: An array of (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) defining the crop bounds,
where these values are absolute pixel coordinates in the image.
Returns:
- Cropped image as a 2D numpy array.
"""
x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max = bounds
return image[y_min:y_max, x_min:x_max]
Calculate signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)#
Compute the SNR between the original and modified images.
def calculate_snr(original, modified):
"""
Compute the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) between the original and modified images.
Parameters:
- original: The original image as a 2D numpy array.
- modified: The modified (rotated) image as a 2D numpy array.
Returns:
- SNR value as a float.
"""
original_normalized = original / 255.0 if original.max() > 1 else original
processed_normalized = modified / 255.0 if modified.max() > 1 else modified
noise = original_normalized - processed_normalized
mean_signal = np.mean(original_normalized)
variance_noise = np.var(noise)
epsilon = 1e-3
snr = 10 * np.log10((mean_signal**2) / (variance_noise + epsilon))
return snr
Calculate mean squared error (MSE)#
Compute the MSE between the original and modified images.
def calculate_mse(original, modified):
"""
Compute the mean squared error (MSE) between the original and modified images.
Parameters:
- original: The original image as a 2D numpy array.
- modified: The modified (rotated) image as a 2D numpy array.
Returns:
- MSE value as a float.
"""
mse = np.mean((original - modified) ** 2)
return mse
Rotate image and crop using SplineOps#
Rotate an image by a specified angle using the splineops library’s TensorSpline method and crop the result.
def rotate_image_and_crop_splineops(image, angle, degree=3, mode="zero", iterations=1):
"""
Rotate an image by a specified angle using the splineops library's TensorSpline method and crop the result.
Parameters:
- image: The input image as a 2D numpy array.
- angle: The rotation angle in degrees.
- degree: The degree of the spline (0-7).
- mode: The mode for handling boundaries (default is "zero").
- iterations: The number of iterations to apply the rotation.
Returns:
- Rotated image as a 2D numpy array.
"""
dtype = image.dtype
ny, nx = image.shape
xx = np.linspace(0, nx - 1, nx, dtype=dtype)
yy = np.linspace(0, ny - 1, ny, dtype=dtype)
data = np.ascontiguousarray(image, dtype=dtype)
rotated_image = data
degree = max(0, min(degree, 7))
basis = f"bspline{degree}"
for _ in range(iterations):
tensor_spline = TensorSpline(
data=rotated_image, coordinates=(yy, xx), bases=basis, modes=mode
)
angle_rad = np.radians(-angle)
cos_angle, sin_angle = np.cos(angle_rad), np.sin(angle_rad)
original_center_x, original_center_y = (nx - 1) / 2.0, (ny - 1) / 2.0
oy, ox = np.ogrid[0:ny, 0:nx]
ox = ox - original_center_x
oy = oy - original_center_y
nx_coords = cos_angle * ox + sin_angle * oy + original_center_x
ny_coords = -sin_angle * ox + cos_angle * oy + original_center_y
eval_coords = ny_coords.flatten(), nx_coords.flatten()
interpolated_values = tensor_spline(coordinates=eval_coords, grid=False)
rotated_image = interpolated_values.reshape(ny, nx)
return rotated_image
Rotate image and crop using SciPy#
Rotate an image by a specified angle using SciPy’s ndimage.rotate function and crop the result.
def rotate_image_and_crop_scipy(image, angle, order=3, iterations=5):
"""
Rotate an image by a specified angle using SciPy's ndimage.rotate function and crop the result.
Parameters:
- image: The input image as a 2D numpy array.
- angle: The rotation angle in degrees.
- order: The order of the spline (0-5).
- iterations: The number of iterations to apply the rotation.
Returns:
- Rotated image as a 2D numpy array.
"""
rotated_image = image.copy()
for _ in range(iterations):
rotated_image = ndimage.rotate(
rotated_image, angle, reshape=False, order=order, mode="constant", cval=0
)
return rotated_image
Benchmark and display rotation#
Perform a benchmark of the rotation operation for both SplineOps and SciPy libraries and display images.
def benchmark_and_display_rotation(image, angle, degree, iterations):
"""
Perform a benchmark of the rotation operation for both splineops and SciPy libraries and display images.
Parameters:
- image: The input image as a 2D numpy array.
- angle: The rotation angle in degrees.
- degree: The degree of the spline (0-7).
- iterations: The number of iterations to apply the rotation.
"""
start_time_custom = time.time()
custom_rotated_and_cropped_splineops = rotate_image_and_crop_splineops(
image, angle, degree=degree, mode="zero", iterations=iterations
)
time_custom = time.time() - start_time_custom
start_time_scipy = time.time()
scipy_rotated_and_cropped = rotate_image_and_crop_scipy(
image, angle, order=degree, iterations=iterations
)
time_scipy = time.time() - start_time_scipy
bounds = calculate_inscribed_rectangle_bounds_from_image(image)
image_cropped = crop_image_to_bounds(image, bounds)
custom_rotated_and_cropped_splineops = crop_image_to_bounds(
custom_rotated_and_cropped_splineops, bounds
)
scipy_rotated_and_cropped = crop_image_to_bounds(scipy_rotated_and_cropped, bounds)
snr_splineops = calculate_snr(image_cropped, custom_rotated_and_cropped_splineops)
snr_scipy = calculate_snr(image_cropped, scipy_rotated_and_cropped)
mse_splineops = calculate_mse(image_cropped, custom_rotated_and_cropped_splineops)
mse_scipy = calculate_mse(image_cropped, scipy_rotated_and_cropped)
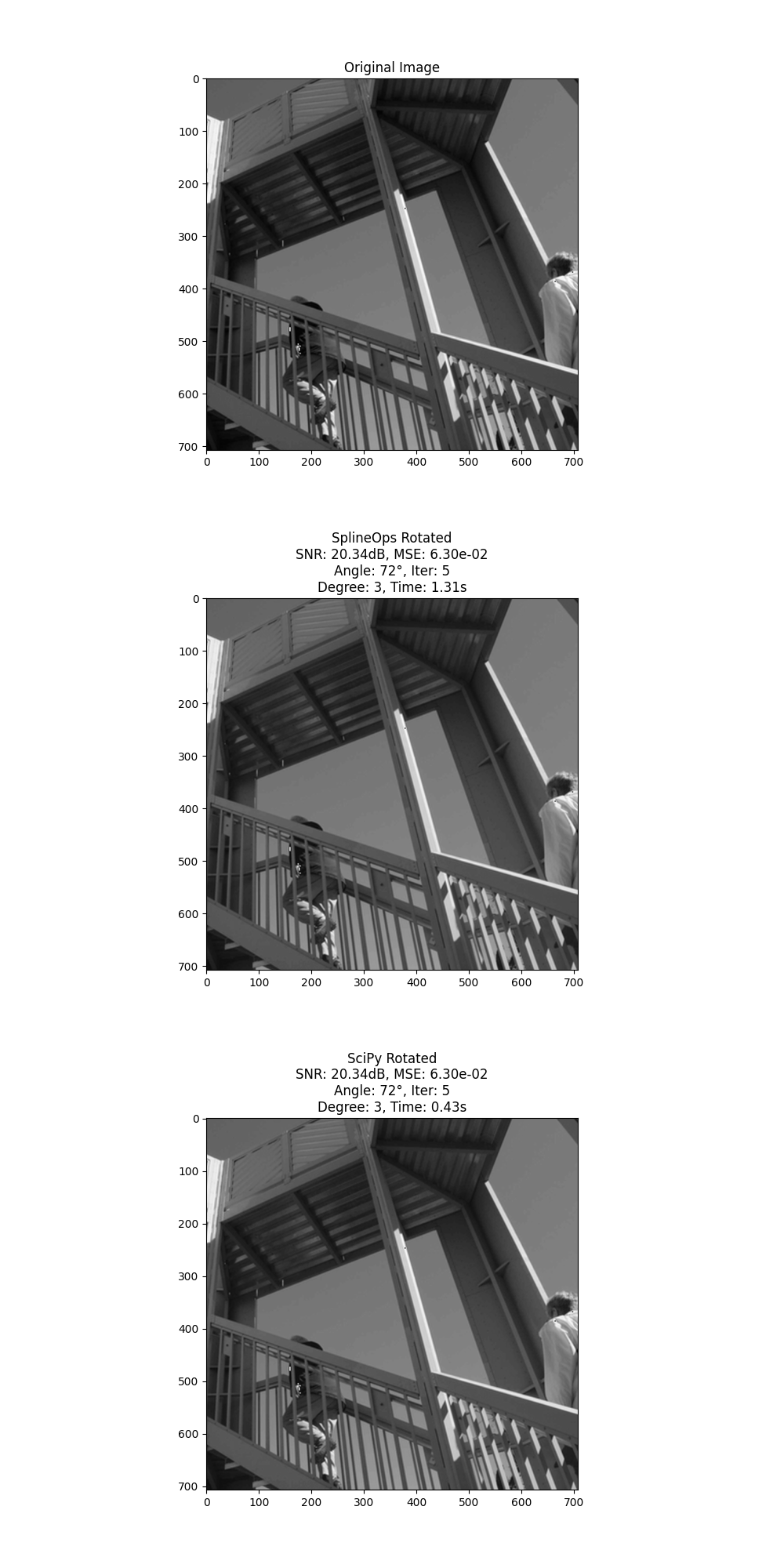
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=1, figsize=(10, 20))
axes[0].imshow(image_cropped, cmap="gray")
axes[0].set_title("Original Image")
axes[1].imshow(custom_rotated_and_cropped_splineops, cmap="gray")
axes[1].set_title(
f"SplineOps Rotated\nSNR: {snr_splineops:.2f}dB, MSE: {mse_splineops:.2e}\nAngle: {angle}°, Iter: {iterations}\nDegree: {degree}, Time: {time_custom:.2f}s"
)
axes[2].imshow(scipy_rotated_and_cropped, cmap="gray")
axes[2].set_title(
f"SciPy Rotated\nSNR: {snr_scipy:.2f}dB, MSE: {mse_scipy:.2e}\nAngle: {angle}°, Iter: {iterations}\nDegree: {degree}, Time: {time_scipy:.2f}s"
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.4, top=0.95, bottom=0.05)
plt.show()
Load image and perform rotations#
Load the image, perform rotations using both SplineOps and SciPy methods, and display the results.
# Image size, Rotation angle and iterations and degree of spline interpolation
size = 1000
angle = 72 # 72
iterations = 5 # 5
degree = 3
# Load and resize the ascent image
image = datasets.ascent()
image_resized = ndimage.zoom(
image, (size / image.shape[0], size / image.shape[1]), order=degree
)
# Convert to float32
image_resized = image_resized.astype(np.float32)
# Benchmark and display rotation results
benchmark_and_display_rotation(image_resized, angle, degree, iterations)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.282 seconds)
