Differentiate Module#
In this example, we demonstrate how to use the differentiate module to compute various differential operations on an image.
You can download this example at the tab at right (Python script or Jupyter notebook.
Imports#
Import the necessary libraries and modules.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
import requests
from io import BytesIO
from PIL import Image
# Import the Differentials class from your module (adjust import path as needed)
from splineops.differentiate.differentials import differentials
Data Preparation#
We retrieve an example color image, convert it to grayscale, and normalize its intensities to the [0,1] range.
url = 'https://r0k.us/graphics/kodak/kodak/kodim15.png'
response = requests.get(url)
img = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content))
image = np.array(img, dtype=np.float64)
# Convert to [0,1]
image_normalized = image / 255.0
# Convert to grayscale via simple weighting
image_gray = (
image_normalized[:, :, 0] * 0.2989 +
image_normalized[:, :, 1] * 0.5870 +
image_normalized[:, :, 2] * 0.1140
)
Helper Visualization Functions#
def show_result_with_colorbar(title, result, units="Value", percentile_range=(5, 95)):
"""
Displays a 2D result with a colorbar scaled using the given percentile range.
Parameters
----------
title : str
Title for the plot.
result : ndarray
2D array representing the image or field to display.
units : str
Label for the colorbar (e.g., 'Intensity', 'Radians', etc.).
percentile_range : tuple or None
Percentiles to use for scaling the colormap. If None, use the min and max of the data.
"""
h, w = result.shape
aspect_ratio = h / float(w)
fig_width = 6.0
fig_height = fig_width * aspect_ratio
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(fig_width, fig_height))
# Determine vmin and vmax based on percentiles if provided
if percentile_range is not None:
pmin, pmax = np.percentile(result, percentile_range)
im = ax.imshow(result, cmap='gray', aspect='equal', vmin=pmin, vmax=pmax)
cbar_label = f"{units} range [{pmin:.3f}, {pmax:.3f}]"
else:
vmin, vmax = result.min(), result.max()
im = ax.imshow(result, cmap='gray', aspect='equal', vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax)
cbar_label = f"{units} range [{vmin:.3f}, {vmax:.3f}]"
ax.set_title(title)
ax.axis('off')
# Create a colorbar with matching height using make_axes_locatable
divider = make_axes_locatable(ax)
cax = divider.append_axes("right", size="5%", pad=0.05)
cbar = plt.colorbar(im, cax=cax)
cbar.set_label(cbar_label)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
def show_angle_result(title, angle_data, vmin, vmax, units="Radians"):
"""
Displays angle data in a cyclical color map (hsv), with vmin and vmax specifying
the circular range.
Parameters
----------
title : str
Title for the plot.
angle_data : ndarray
2D array of angles (in radians).
vmin : float
Minimum of angle range (e.g., 0).
vmax : float
Maximum of angle range (e.g., 2*pi).
units : str
Label for the colorbar (e.g., 'Direction (radians)', etc.).
"""
h, w = angle_data.shape
aspect_ratio = h / float(w)
fig_width = 6.0
fig_height = fig_width * aspect_ratio
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(fig_width, fig_height))
# Plot with an HSV cyclical colormap
im = ax.imshow(angle_data, cmap='hsv', aspect='equal', vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax)
ax.set_title(title)
ax.axis('off')
# Add colorbar
divider = make_axes_locatable(ax)
cax = divider.append_axes("right", size="5%", pad=0.05)
cbar = plt.colorbar(im, cax=cax, ticks=[vmin, (vmin+vmax)/2, vmax])
cbar.set_label(f"{units} range [{vmin:.2f}, {vmax:.2f}]")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
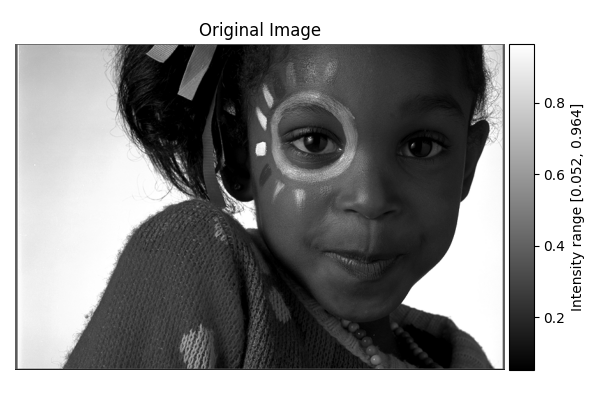
Show the original grayscale image with a colorbar
show_result_with_colorbar("Original Image", image_gray, units="Intensity")

Gradient Magnitude#
diff = differentials(image_gray.copy())
diff.run(differentials.GRADIENT_MAGNITUDE)
grad_magnitude_result = diff.image
show_result_with_colorbar("Gradient Magnitude", grad_magnitude_result, units="Value")
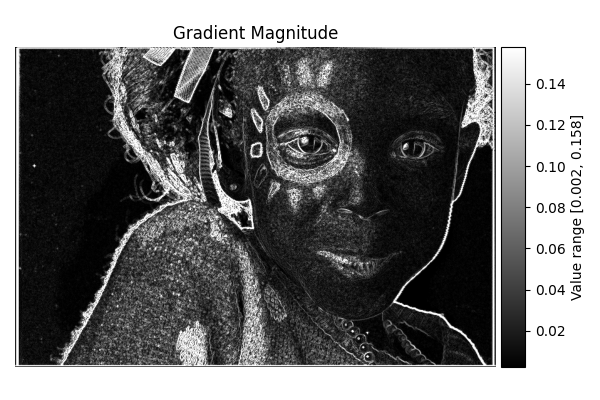
Completed in 1.21 seconds
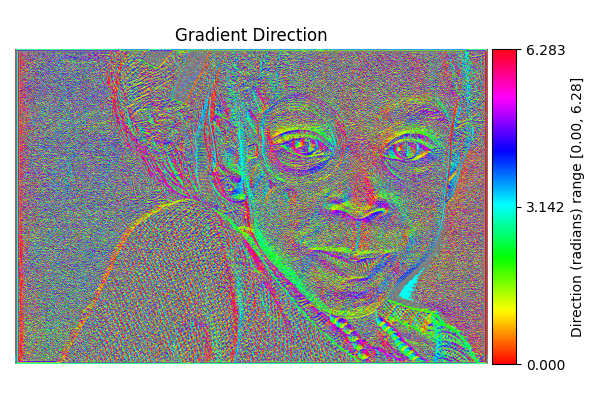
Gradient Direction#
diff = differentials(image_gray.copy())
diff.run(differentials.GRADIENT_DIRECTION)
grad_direction_result = diff.image
# Shift from [-π, π] to [0, 2π]
grad_direction_result_0_2pi = (grad_direction_result + 2.0*np.pi) % (2.0*np.pi)
# Visualize with HSV colormap, removing percentile clipping
show_angle_result(
"Gradient Direction",
grad_direction_result_0_2pi,
vmin=0.0, vmax=2.0*np.pi,
units="Direction (radians)"
)

Completed in 1.23 seconds
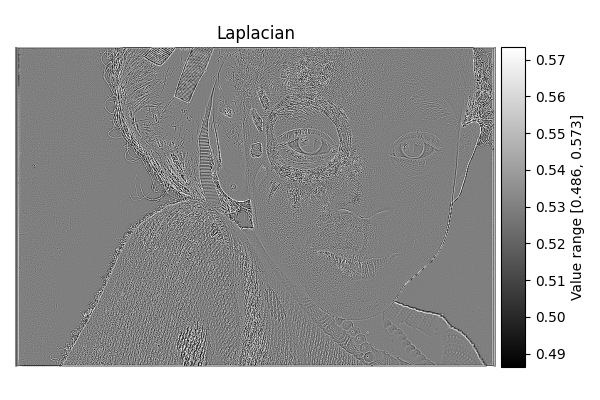
Laplacian#
diff = differentials(image_gray.copy())
diff.run(differentials.LAPLACIAN)
laplacian_result = diff.image
show_result_with_colorbar("Laplacian", laplacian_result, units="Value")

Completed in 1.44 seconds
Largest Hessian#
diff = differentials(image_gray.copy())
diff.run(differentials.LARGEST_HESSIAN)
largest_hessian_result = diff.image
show_result_with_colorbar("Largest Hessian Eigenvalue", largest_hessian_result, units="Value")
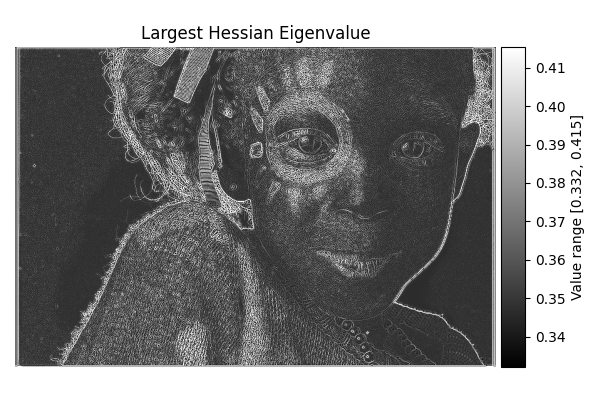
Completed in 2.65 seconds
Smallest Hessian#
diff = differentials(image_gray.copy())
diff.run(differentials.SMALLEST_HESSIAN)
smallest_hessian_result = diff.image
show_result_with_colorbar("Smallest Hessian Eigenvalue", smallest_hessian_result, units="Value")
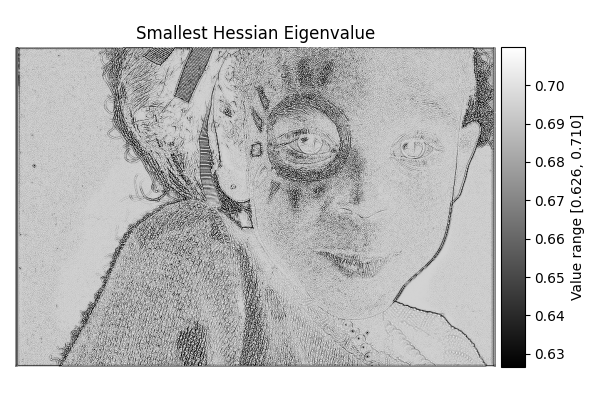
Completed in 2.65 seconds
Hessian Orientation#
diff = differentials(image_gray.copy())
diff.run(differentials.HESSIAN_ORIENTATION)
hessian_orientation_result = diff.image
show_angle_result(
"Hessian Orientation",
hessian_orientation_result,
vmin=-np.pi/2.0, vmax=np.pi/2.0,
units="Orientation (radians)"
)
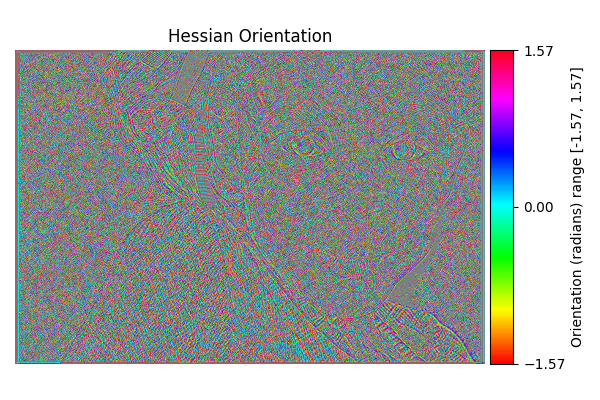
Completed in 2.67 seconds
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 14.357 seconds)
