1D Fractional Brownian Motion#
We use the smooth module to smooth a 1D fractional Brownian motion signal.
Imports#
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from splineops.denoise.fBmper import fBmper
from splineops.denoise.smoothing_spline import smoothing_spline
1D Fractional Brownian Motion#
A realization of an fBm process of length N is generated and corrupted with noise. The sequence is then denoised and oversampled by a factor m using the optimal fractional-spline estimator.
# Define program constants
m = 4 # Upsampling factor
N = 256 # Number of samples
# Default values
default_H = 0.7
default_SNRmeas = 20.0
default_verify = '0'
# Enter Hurst parameter [0 < H < 1] (default: 0.7) >
H = 0.7
# Enter measurement SNR at the mid-point (t = {N/2}) [dB] (default: 20.0) >
SNRmeas = 20.0
# Create pseudo-fBm signal
epsH = 1
t0, y0 = fBmper(epsH, H, m, N)
Ch = epsH ** 2 / (math.gamma(2 * H + 1) * np.sin(np.pi * H))
POWmid = Ch * (N / 2) ** (2 * H) # Theoretical fBm variance at the midpoint
# Measurement: downsample and add noise
t = t0[::m]
y = y0[::m]
sigma = np.sqrt(POWmid) / (10 ** (SNRmeas / 20))
noise = np.random.randn(N)
noise = sigma * noise / np.sqrt(np.mean(noise ** 2))
y_noisy = y + noise
# Find smoothing spline fit
lambda_ = (sigma / epsH) ** 2
gamma_ = H + 0.5
ts, ys = smoothing_spline(y_noisy, lambda_, m, gamma_)
# Add non-stationary correction term
cnn = np.concatenate(([1], np.zeros(N - 1))) # Normalized white noise autocorrelation
tes, r = smoothing_spline(cnn, lambda_, m, gamma_)
r = r * ys[0] / r[0]
y_est = ys - r
# Calculate MSE and SNR
MSE0 = np.mean(noise ** 2) # Measurement MSE
MSE = np.mean((y_est[::m] - y0[::m]) ** 2) # Denoised sequence MSE
MSEm = np.mean((y_est - y0) ** 2) # Denoised and oversampled signal MSE
SNR0 = 10 * np.log10(POWmid / MSE0)
SNR = 10 * np.log10(POWmid / MSE)
SNRm = 10 * np.log10(POWmid / MSEm)
print(f'Number of measurements is {N}, oversampling factor is {m}.')
print(f'mSNR (SNR at the mid-point) of the measured sequence is {SNR0:.2f} dB.')
print(f'mSNR improvement of the denoised sequence is {SNR - SNR0:.2f} dB.')
print(f'mSNR improvement of the denoised and oversampled sequence is {SNRm - SNR0:.2f} dB.')
# Plot the results
plt.figure()
plt.plot(t0[:len(t0)//2], y0[:len(y0)//2], 'k', label='fBm')
plt.plot(t[:len(t)//2], y_noisy[:len(y_noisy)//2], 'k+:', label='Noisy fBm samples')
plt.plot(ts[:len(ts)//2], ys[:len(ys)//2], 'r--', label='Stationary estimation')
plt.plot(tes[:len(tes)//2], y_est[:len(y_est)//2], 'r', label='Non-stationary estimation')
plt.legend()
plt.title(f'Estimation of fBm (H = {H}, ε_H^2 = {epsH}, σ_N^2 = {sigma ** 2:.4f})')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('B_H')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
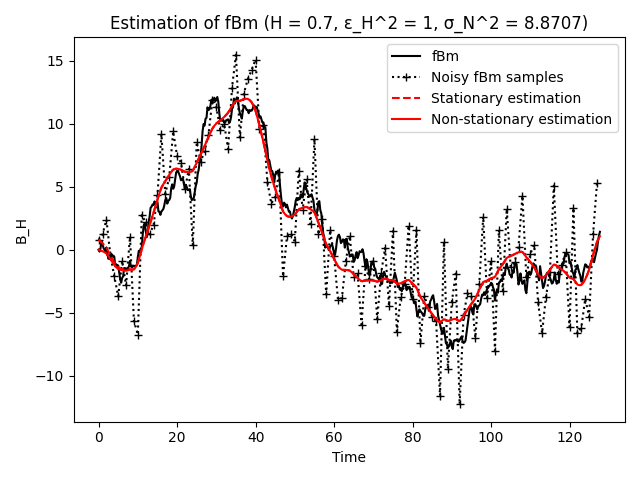
Number of measurements is 256, oversampling factor is 4.
mSNR (SNR at the mid-point) of the measured sequence is 20.00 dB.
mSNR improvement of the denoised sequence is 7.57 dB.
mSNR improvement of the denoised and oversampled sequence is 7.71 dB.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.157 seconds)
